オリジナル記事:Hubble Spins a Web Into a Giant Red Spider Nebula
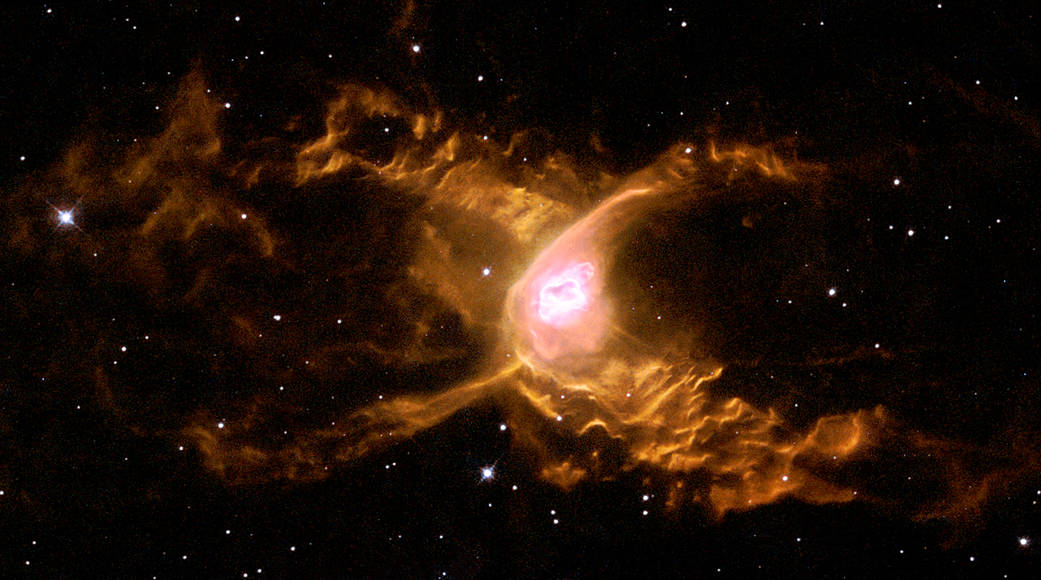
Huge waves are sculpted in this two-lobed nebula called the Red Spider Nebula, located some 3,000 light-years away in the constellation of Sagittarius. This warm planetary nebula harbors one of the hottest stars known and its powerful stellar winds generate waves 100 billion kilometers (62.4 billion miles) high. The waves are caused by supersonic shocks, formed when the local gas is compressed and heated in front of the rapidly expanding lobes. The atoms caught in the shock emit the spectacular radiation seen in this image.
Text credit: ESA (European Space Agency)
Image credit: ESA/Garrelt Mellema (Leiden University, the Netherlands)
Last Updated: Oct. 21, 2016
Editor: Rob Garner
ハッブルで見た巨大なトレッドスパイダー星雲
3000光年の距離にある射手座に位置するレッドスパイダー星雲に、丸みを帯びた2つの星雲が巨大な波のような形を作っています。この暖かい惑星状星雲は、高温の星々を抱えており、千億キロ(624億マイル)に及ぶ高さの強力な恒星風の波を作り出しているのです。局所に溜まったガスが急速に拡大する星雲の摩擦熱で加熱・圧縮されて生じた超音波の衝撃が、波を引き起こしています。衝撃に巻き込まれた原子が膨大な放射線を放出しているのが、この画像です。
訳者注:
「今日の1枚」は、画像も文章も欧州宇宙機関とオランダのライデン大学のものとのことで、NASAとしてもコメントも何もありませんでした。