オリジナル記事:One Billion Base Pairs Sequenced on the Space Station
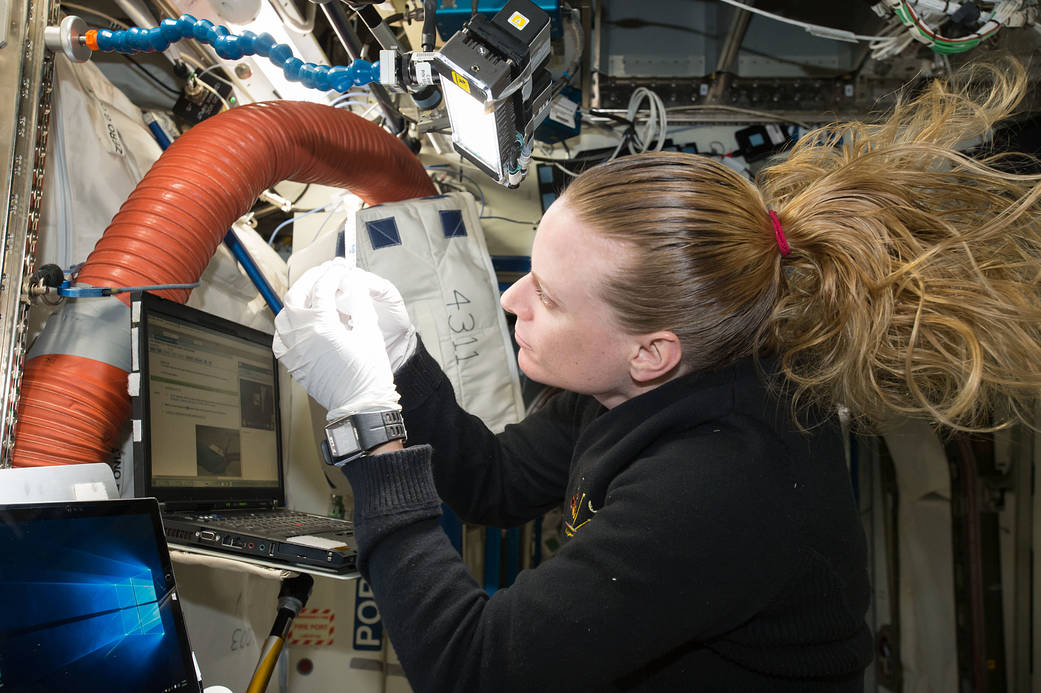
Aboard the International Space Station, NASA astronaut Kate Rubins checks a sample for air bubbles prior to loading it in the biomolecule sequencer. When Rubins’ expedition began, zero base pairs of DNA had been sequenced in space. Within just a few weeks, she and the Biomolecule Sequencer team had sequenced their one billionth base of DNA on the orbiting laboratory.
“I [have a] genomics background, [so] I get really excited about that kind of stuff,” Rubins said in a downlink shortly after reaching the one billion base pairs sequenced goal.
The Biomolecule Sequencer investigation seeks to demonstrate that DNA sequencing in microgravity is possible, and adds to the suite of genomics capabilities aboard the space station. With a way to sequence DNA in space, astronauts could diagnose an illness, or identify microbes growing in the International Space Station and determine whether or not they represent a health threat. A space-based DNA sequencer would be an important tool to help protect astronaut health during long duration missions on the journey to Mars, and future explorers could also potentially use the technology to identify DNA-based life forms beyond Earth.
Image Credit: NASA
Last Updated: Sept. 22, 2016
Editor: Sarah Loff
宇宙ステーションで一億の塩基対を作成
国際宇宙ステーションに滞在しているNASAの宇宙飛行士ケイト・ルビンズは、気泡を使って生体分子シーケンサーの事前チェックをしています。ルビンズの滞在が始まった時には、宇宙空間にDNA塩基対はゼロでした。そのわずか数週間後には、彼女と生体分子シーケンサーチームは実験棟でのDNA塩基対を数億にしたのです。
「私にはゲノムについての知識はあるけど、これには本当に興奮したわ。」と、ルビンズは目標としていた10億の塩基対の生成に達した後にダウンリンクでコメントしています。
生体分子シーケンサーによる調査は、微小重力環境下におけるDNA配列調査が可能であることと、宇宙ステーションにゲノム機能を追加することの実証実験です。宇宙でのDNA検査は、宇宙飛行士の病気診断や、国際宇宙ステーション内で成長している微生物を特定し、それらが健康に脅威となるかかどうかを調査することができます。宇宙空間でのDNAシーケンサーは、火星への旅のために長時間の任務にあたる宇宙飛行士の健康を保護するための重要な道具であり、今後の探査活動において地球外生命体のDNAによる分析をするために使用する技術でもあるのです。
訳者注
割とあっさりとした記事ですが、もうじき始まる火星有人探査で有機体(つまり地球外生命体)を検査する手法の確認しているという結構スゴイことですね。